Information Maximizing Clinical Diagnostics
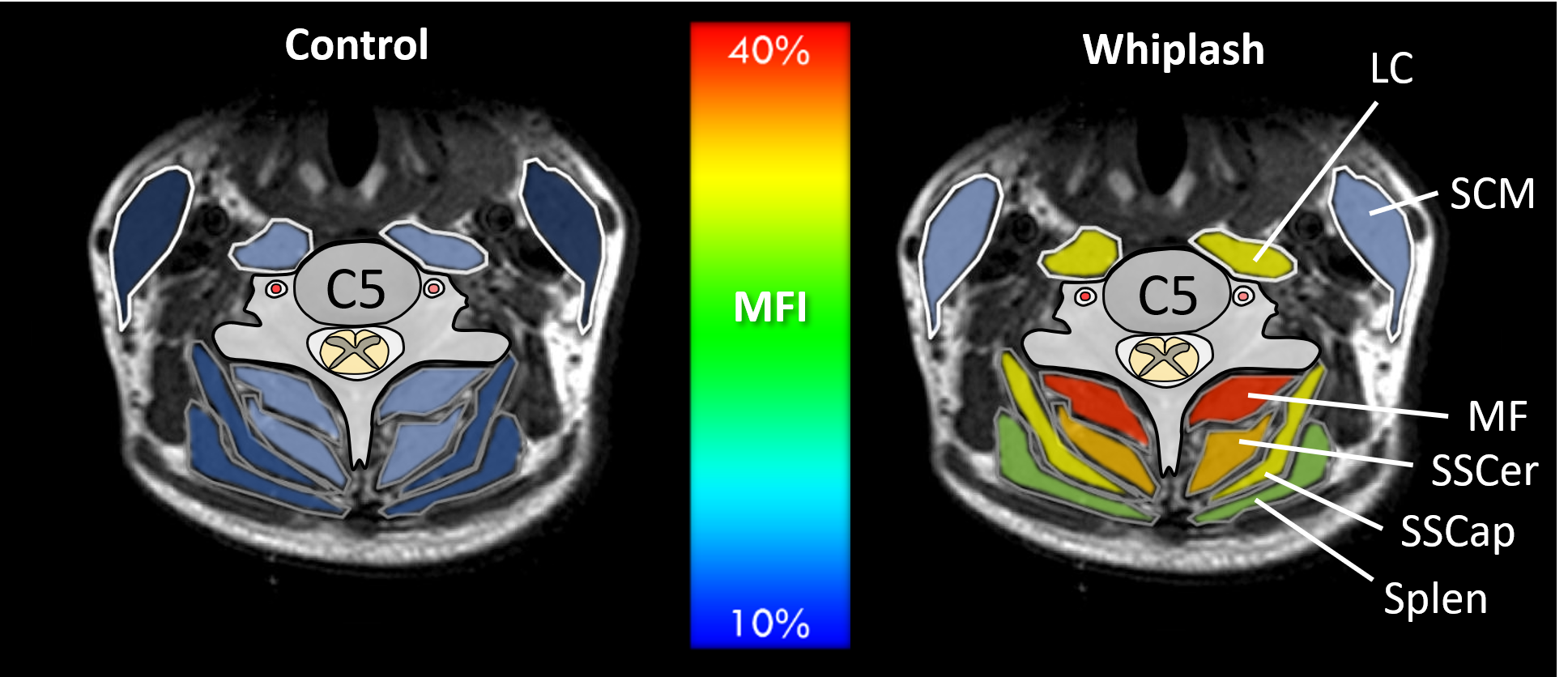
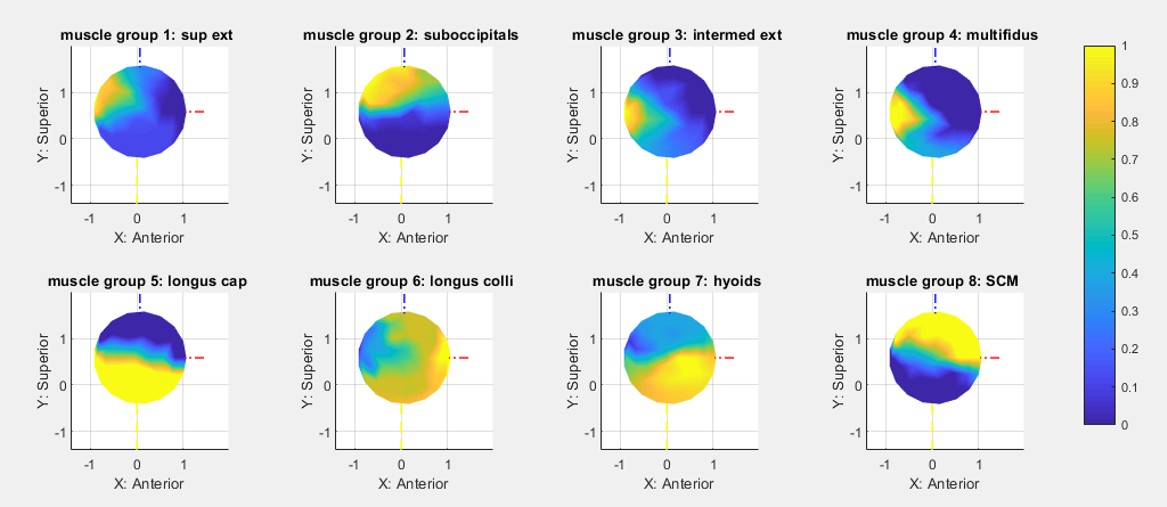
Kinematic and muscular redundancy in the human musculoskeletal system makes it difficult to evaluate the function of specific muscle groups. The neck is particularly challenging, with seven cervical vertebrae and more than 20 muscle groups. Muscle atrophy of the deep neck extensor muscles has been identified using quantitative Magnetic Resonance imaging in individuals with chronic whiplash disorders. However, the biomechanical consequences of weakness to his muscle group is unknown. In this work, we develop utilize musculoskeletal models, Bayesian inference, and information theory to develop a testing algorithm to efficiently estimate the strength of individual muscle groups of the neck through physical strength testing.
People
Rebecca Abbott (Ph.D. Student)
Collaborators
James Elliott, University of Sydney
Publications
The qualitative grading of muscle fat infiltration in whiplash using fat and water magnetic resonance imaging
R. Abbott, A Peolsson, J. West, J. Elliott, U Aslund, A Karlsson, O Dahlqvist Leinhard
The Spine Journal, vol. 18, pp. 717-725, 2018. Paper
Manually defining regions of interest when quantifying paravertebral muscles fatty infiltration from axial magnetic resonance imaging: a proposed method for the lumbar spine with anatomical cross-reference
R. Crawford, J Cornwall, R. Abbott, J. Elliott
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, vol. 18, no. 25, 2017. Paper
Towards defining muscular regions of interest from axial magnetic resonance imaging with anatomical cross-reference: part II - cervical spine musculature
J. Elliott, J Cornwall, E Kennedy, R. Abbott, R. Crawford
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, vol. 19, no. 1, 2017. Paper
The geography of fatty infiltrates within the cervical multifidus and semispinalis cervicis in individuals with chronic whiplash-associated disorders
R. Abbott, A. Pedler, M. Sterling, J. Hides, T. D. Murphey, M. Hoggarth, and J. Elliott
Journal of Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy, vol. 45, no. 4, pp. 281–288, 2015.
Muscle-Fat MRI: 1.5 Tesla and 3.0 Tesla versus histology
A. Smith, T Parrish, R. Abbott, M. Hoggarth, K. Mendoza, Y. Chen, J. Elliott
Muscle & Nerve, vol. 50, pp. 170-176, 2014. Paper
Funding
This project is funded by National Institute of Health grant T32 EB009406.
Other Projects
Active Learning and Data-Driven Control
Active Perception in Human-Swarm Collaboration
Algorithmic Matter and Emergent Computation
Control for Nonlinear and Hybrid Systems
Cyber Physical Systems in Uncertain Environments
Harmonious Navigation in Human Crowds
Information Maximizing Clinical Diagnostics
Reactive Learning in Underwater Exploration
Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation
Software-Enabled Biomedical Devices