Software-Enabled Biomedical Devices
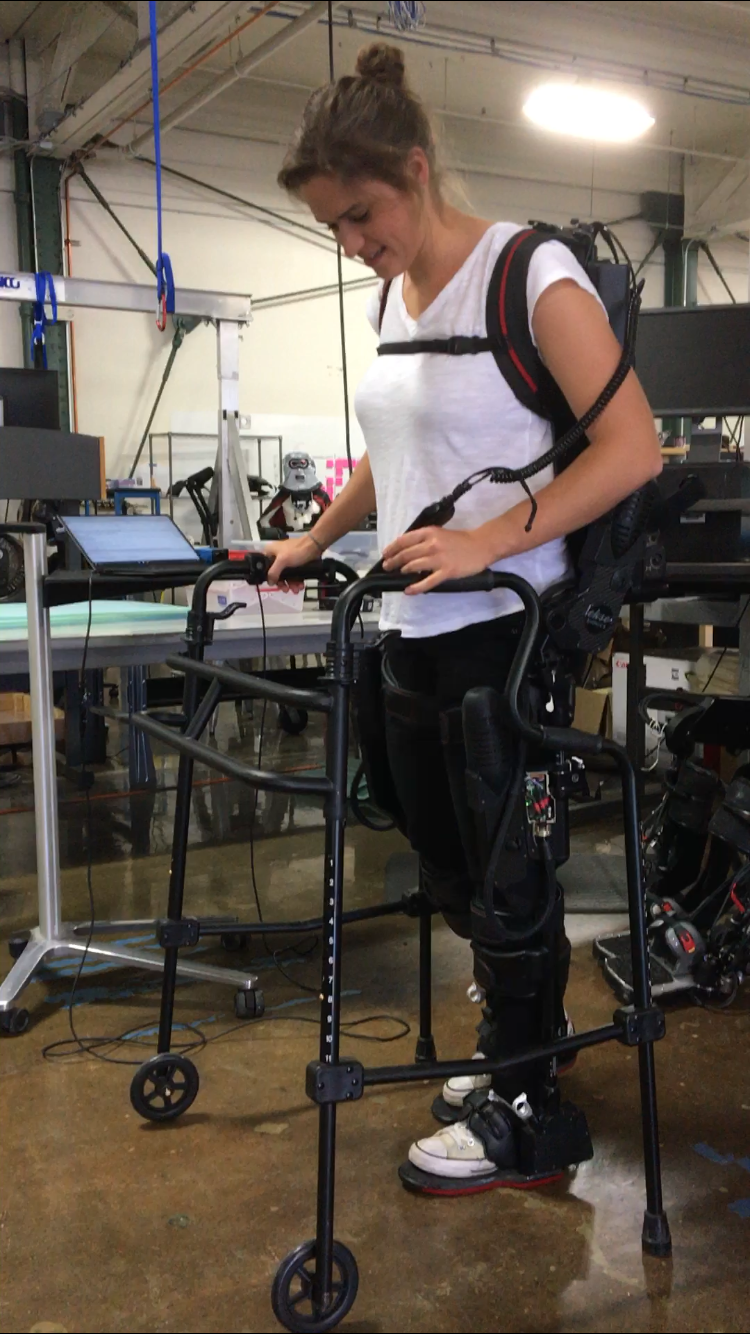

A lower-limb Ekso Bionics exoskeleton
Simulated lunar lander
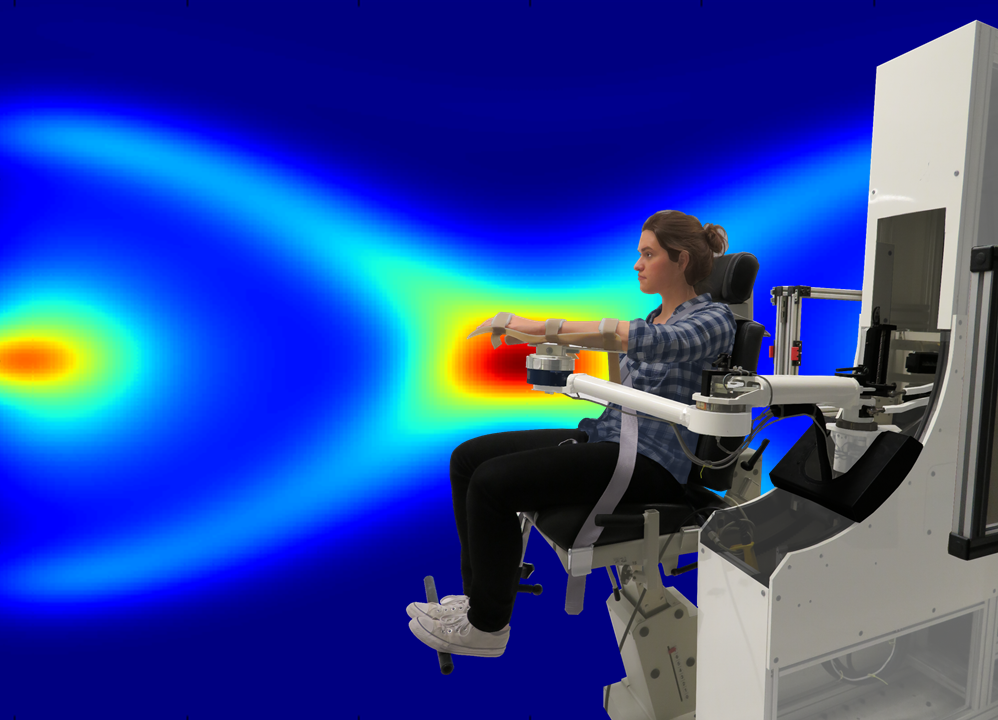

Human-machine interaction
Assistive devices are intended to enable users to learn motion in a safe and effective manner or to accomplish tasks they wouldn't be able to perform on their own (e.g. due to injury or degeneration). In this work we develop algorithms for task-specific support of motion, specifically considering dynamic tasks, where reaction time is critical to the success of the task. We aim to create software that ensures efficacy and safety, while leaving room for the user to be in control and/or exert effort. We test our algorithms in three different experimental testbeds:
• virtual environments, such as a simulated car or Lunar Lander,
• an upper-limb assistive device (NACT-3D),
• and a lower-limb Ekso Bionics exoskeleton.
People
Tommy Berrueta (Ph.D. Student)
Katie Fitzsimons (Ph.D. Student)
Ola Kalinowska (Ph.D. Student)
Milli Schlafly (Ph.D. Student)
Collaborators
Brenna Argall, Northwestern University
Julius Dewald, Northwestern University
Ekso Bionics
Publications
Ergodic imitation: Learning from what to do and what not to do
A. Kalinowska, A. Prabhakar, K. Fitzsimons, T. D. Murphey
IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2021. PDF
Task-based hybrid shared control for training through forceful interaction
K. Fitzsimons, A. Kalinowska, J. Dewald and T. D. Murphey
International Journal of Robotics Research, 2020. PDF
Ergodicity reveals assistance and learning in physical human robot interaction
K. Fitzsimons, A. M. Acosta, J. Dewald, and T. D. Murphey
Science Robotics, vol. 4, no. 29, 2019.
Dynamical system segmentation for information measures in motion
T. Berrueta, A. Pervan, K. Fitzsimons, and T. Murphey
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 169–176, 2019. PDF
Data-driven gait segmentation for walking assistance in a lower-limb assistive device
A. Kalinowska, T. Berrueta, A. Zoss, and T. D. Murphey
IEEE Int. Conf. on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2019. PDF
Operation and imitation under safety-aware shared control
A. Broad, T. Murphey, and B. Argall
Workshop on the Algorithmic Foundations of Robotics (WAFR), 2018. PDF
Online user assessment for minimal intervention during task-based robotic assistance
A. Kalinowska, K. Fitzsimons, J. Dewald, and T. D. Murphey
Robotics: Science and Systems Proceedings, 2018. PDF
Funding
This project is funded by the National Science Foundation–National Robotics Initiative: Task-Based Assistance for Software-Enabled Biomedical Devices
Other Projects
Active Learning and Data-Driven Control
Active Perception in Human-Swarm Collaboration
Algorithmic Matter and Emergent Computation
Control for Nonlinear and Hybrid Systems
Cyber Physical Systems in Uncertain Environments
Harmonious Navigation in Human Crowds
Information Maximizing Clinical Diagnostics
Reactive Learning in Underwater Exploration
Robot-Assisted Rehabilitation
Software-Enabled Biomedical Devices